.xml로 끝나는 확장자는 모두 객체(bean)을 정의함.
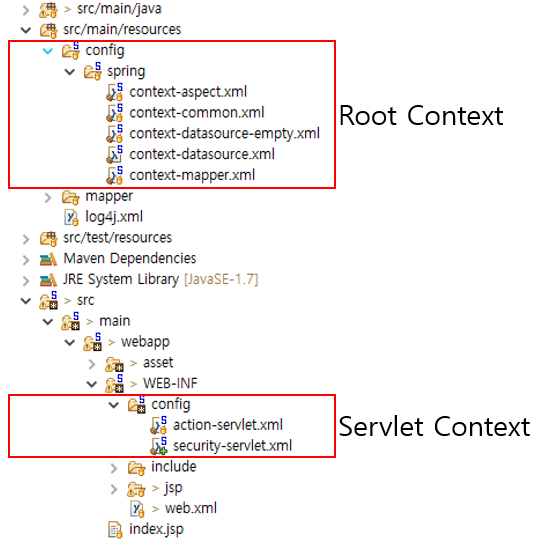
1. servlet-contex.xml
|
JSP와 관련있는 객체(bean) 설정 - controller, MultipartResolver, Interceptor(로그인 등) |
|
WEB Application 에서 client 요청을 받기 위한 설정 |
|
어노테이션 <annotation-driven/> |
|
URL 관련 설정 |
servlet에서 보듯이 요청과 관련된 객체를 정의
url과 관련된 controller나, @(어노테이션), ViewResolver, Interceptor, MultipartResolver 등의 설정
<!-- DispatcherServlet Context: defines this servlet's request-processing infrastructure -->
위와 같은 주석이 있는데,,
DispatcherServlet과 관련된 설정을 해야함을 알 수 있습니다.
2. root-contex.xml
|
JSP와 관련없는 객체(bean)을 설정합니다.(service, repository) |
|
비지니스 로직을 위한 설정을 합니다. |
|
외부 jar 파일등으로 사용하는 클래스는 <bean>태그를 이용하여 작성합니다. |
|
공통 빈을 설정합니다. |
따라서 Service, Repository(DAO), DB등 비즈니스 로직과 관련된 설정servlet-context.xml 과는 반대로 view와 관련되지 않은 객체를 정의

(출처: https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web.html#mvc)
3. web.xml
설정을 위한 설정파일입니다.
즉, 최초로 WAS가 최초로 구동될 때, 각종 설정을 정의해줍니다.
여러 xml파일을 인식하도록 각 파일을 가리켜 줍니다.
(출처 : thiago6.tistory.com/70)
'Framework > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [MyBatis] <!cdata[ 사용이유 (0) | 2021.01.05 |
|---|---|
| [Spring]Annotation 정리 (0) | 2021.01.05 |
| [Spring]sqlsession 사용 유무 Flow 차이점 (0) | 2021.01.05 |


